Aluminum extrusion is becoming an increasingly vital metal forming process in modern industrial manufacturing. From aerospace to construction, from automobiles to electronics, it is almost everywhere.
Today, we will give you a brief introduction to aluminum extrusion. This is an amazing manufacturing process.

What is Aluminum Extrusion
Metal extrusion technology started in the late 1700s. Joseph Bramah, an Englishman, invented it in 1797. He created it to make lead pipes.
The industrial application of aluminum extrusion technology, on the other hand, began in the early 20th century. With the progress of aluminum smelting technology and cost reduction, aluminum extrusion has developed rapidly and become an important metal processing method.
Aluminum extrusion is a metal shaping process. It involves applying high temperature and pressure to aluminum alloy. This process makes the aluminum go through a die with a certain shape. The result is a continuous piece with a specific cross-sectional profile.
This process can create solid and hollow profiles. It can also make structural parts with complex shapes. Many industries use it, such as construction, automotive, aerospace, rail transportation, and electronics.
The principle of aluminum extrusion is similar to squeezing toothpaste from a tube. During this process, a die pushes aluminum out. This creates a profile in the shape we want.
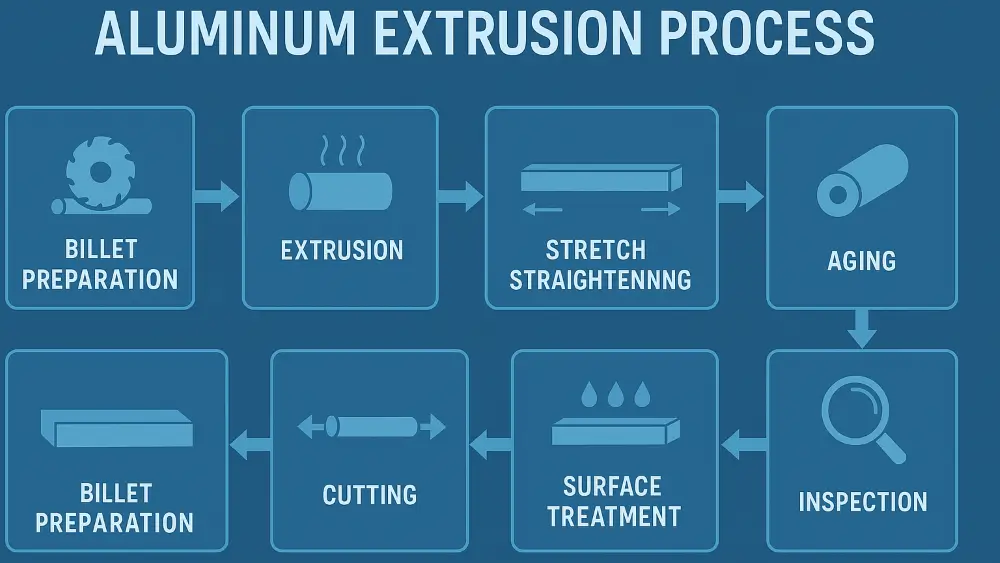
Core Steps of Aluminum Extrusion
The main idea of aluminum extrusion is to use the metal’s ability to change shape. This occurs when someone heats aluminum alloy and pushes it into a die. The core steps include:
- Heating the aluminum billet: typically to 400°C – 500°C to increase plasticity and reduce resistance to deformation.
- Applying extrusion pressure: A machine pushes the aluminum bar into the die with a high pressure of 30-100 MPa. You can use hydraulic or mechanical methods to do this.
- Flow forming: The aluminum alloy flows plastically in the die to form the desired cross-sectional structure (e.g. square tubes, round tubes, complex geometries, etc.).
- Cooling and heat treatment: The extruded profile cools with air or water. Some strong alloys need T5 or T6 heat treatment to work better.
- Straightening and surface treatment: Workers straighten the profiles by stretching. After that, you can perform surface treatments like anodizing, electrophoresis, and spraying. These treatments improve corrosion resistance and add a decorative effect.
Aluminum extrusion materials, characteristics and applications
1. High strength requirements (2000, 7000 series)
Applicable to aerospace, military, precision machinery, molds and other fields, need to withstand large loads and high strength requirements.
- 7075 :extremely high strength, commonly used in aircraft structure, military equipment, mountaineering equipment, racing car parts.
- 7050:better corrosion resistance than 7075, suitable for aviation structural parts.
- 2024 :high strength but poor corrosion resistance, commonly used in aircraft skins, fasteners, mechanical parts.
- 2618:excellent high temperature strength, suitable for engine pistons, racing parts.
2. Corrosion resistance needs (5000, 6000 series)
Suitable for applications requiring long-term corrosion resistance, such as marine environments, building structures, outdoor equipment, and automobile shells.
- 5052: Excellent corrosion resistance, widely used in ships, oil tanks, chemical equipment, traffic signs.
- 5083: Even stronger corrosion resistance, especially suitable for marine engineering, ships, pressure vessels.
- 6061: medium strength, good corrosion resistance, can be heat-treated, suitable for automotive parts, aviation components, mechanical structures.
- 6063: excellent corrosion resistance, widely used in building profiles, window frames, radiators.
3. Conductive, thermal conductivity needs (1000 series)
Suitable for electronics, cables, heat dissipation systems, chemical containers, and other applications with high requirements for electrical or thermal conductivity.
- 1050, 1100 : excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, suitable for transformers, conductive rows, heat sinks, aluminum foil.
- 1350: Specialized for high conductivity applications such as wires and cables.
4. Weldability and heat resistance requirements (4000 series)
Suitable for automotive, engine cooling systems, welded structures, and other applications requiring good weldability and heat resistance.
- 4045 (aluminum-silicon alloy): good weldability, commonly used in automotive cooling systems, radiators, heat exchangers.
- 4032:Excellent abrasion resistance and high temperature stability, suitable for engine pistons, air compressor parts.
5. Excellent comprehensive performance (6000 series)
Suitable for applications requiring a balance of strength, corrosion resistance and processing performance, such as construction, machinery manufacturing, rail transportation, structural components.
- 6061:High strength, good corrosion resistance and processability, widely used in mechanical structures, automobile parts, ships, aviation parts.
- 6063:good extrusion performance, high surface finish, suitable for building profiles, decorative materials, aluminum doors and windows.
- 6082:high strength, suitable for bridges, cranes, heavy structural parts.
The main types of aluminum extrusion processes
The aluminum extrusion process has different types. These types depend on the direction of the pressure, die structure, and temperature conditions.
1 Classification according to the direction of extrusion
- Forward Extrusion (Direct Extrusion): The punch of the extruder is in the same direction as the flow of aluminum. Applicable to most industrial aluminum production, but the friction is larger, die wear faster.
- Reverse Extrusion (Indirect Extrusion): the die is fixed, and the aluminum bar moves with the punch. As there is no relative friction between the material and the container wall, energy loss can be reduced and material utilization can be improved.
2 Classification according to temperature
- Hot Extrusion: Extrusion is carried out at 400°C-500°C to give aluminum alloy material better plasticity and fluidity. Suitable for the production of medium and large aluminum profiles, such as building profiles, industrial radiators and so on.
- Cold Extrusion: This process happens at room temperature or low temperatures. Good for making small and precise aluminum parts, like electronic shells and medical equipment parts. Because of the cold work hardening effect, cold extruded products usually have higher strength and hardness.
What are the main shapes that can be made from aluminum extrusion?
Aluminum extrusion is a highly flexible manufacturing process that can produce a variety of cross-sectional shapes on demand. Depending on the design requirements, shapes made by aluminum extrusion can be used in a wide range of industries. The following are some of the common shapes that can be produced by the aluminum extrusion process:
| Category | Typical shape | Main applications |
| Solid profiles | Round bar, square bar, angle aluminum, T profile | Structural components, machine parts |
| Hollow profiles | Round tube, square tube, multi-lumen tube | Automobile frames, building curtain walls |
| Semi-hollow profiles | C-channel, U-channel | Guides, shields |
| Complex section | Multi-cavity broken bridge aluminum, functionally integrated profiles | Energy-saving windows and doors, electronic radiators |
| Special profiles | Heat Sink Fins, Rails, Trim Strips | Industrial equipment, high-end consumer electronics |
Advantages of Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum extrusion has the following significant advantages over other metal processing methods:
- High design freedom: complex cross-section structures can be manufactured to suit different engineering needs.
- High material utilization: Reduces waste and saves production costs.
- High strength and light weight:Especially suitable for aerospace and automotive lightweighting.
- Excellent corrosion resistance:6061, 6063 and other aluminum alloys have good weathering and chemical corrosion resistance after anodic oxidation treatment.
- Sustainability: Aluminum is a 100% recyclable metal, in line with environmental trends.
The future development trend of aluminum extrusion:
- Intelligence and automation: with the development of Industry 4.0, the aluminum extrusion industry will increasingly adopt intelligent and automated technologies. This will improve production efficiency, reduce manual intervention, and enable real-time quality monitoring to ensure the consistency and precision of each batch.
- Environmental protection and energy-saving technologies:As environmental protection requirements increase, the aluminum extrusion process will develop in the direction of energy saving and environmental protection. This includes more efficient heating technology, process improvements to reduce waste generation, and more environmentally friendly materials and equipment.
- Application of high-performance aluminum alloys:In the future, aluminum extrusion will be applied more to new high-performance aluminum alloy materials, which have better strength, corrosion resistance, and lighter weight, and are particularly suitable for aerospace, automotive and other high-end fields.
- Customized production:With the increase in market demand for personalized and customized products, aluminum extrusion process will gradually shift from standardized products to small-lot, high-precision, customized production. This requires the production line to have higher flexibility and rapid response capability.
- Combination of composite materials and aluminum extrusion:In the future, aluminum extrusion may be combined with other materials (e.g., plastics, composites) to create lightweight and more durable products that meet the needs of more fields, especially in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Conclusion
Aluminum extrusion technology, a bridge connecting material science and industrial applications, has grown into an invisible pillar of modern manufacturing after a century of development. From everyday items to advanced aerospace systems, aluminum extrusion is everywhere—though often unseen and underappreciated. Driven by technological advances and the need for sustainable development, this ancient but modern craft will continue to evolve and play an even more critical role in the course of human civilization.
The next time we touch the metal bezel of a smartphone or walk through a glass curtain wall building, we may remember that behind these simple and beautiful lines are countless engineers’ deep understanding and innovative breakthroughs in material behavior, mechanics and manufacturing processes. The journey of aluminum extrusion exemplifies how industrial innovation can transform raw materials into functional works of art.
So, how does aluminum extrusion connect with CNC machining? In the next article, we’ll explore how combining aluminum extrusion with CNC machining unlocks new levels of efficiency and precision.